Image Source: Unsplash
Approximately 50 million people have dementia worldwide, and there are around 10 million new cases of dementia every year. Alzheimer’s disease, the most prevalent type of dementia, accounts for up to 70% of dementia cases.
According to the World Health Organization, “Dementia is a syndrome in which there is deterioration in memory, thinking, behavior and the ability to perform everyday activities.” While dementia is associated with a number of symptoms, the most common ones include changes to personality, loss of memory, trouble focusing, and communication problems with listening and speaking. Dementia often affects older people, but it’s not a normal, expected part of aging.
Risk Factors of Dementia
The reason dementia is so scary is because it can be unavoidable. While some risk factors of dementia can be managed, others can’t. Even if a person is predisposed to dementia because of family history, managing the other risk factors may keep dementia at bay for longer. Here are some of the most common risk factors of dementia:
- Aging: Dementia should not be considered a normal part of aging, but the risk does go up as people age. As a person ages, their brain cells diminish and they experience memory loss, both of which can contribute to dementia.
- Behavioral issues: Depression during middle age can be a risk factor of dementia (not just a symptom, as some people may think). Patients with bipolar or unipolar disease may also have a higher chance of developing dementia. For people who want to treat depression before it worsens, sleeping more may help – prolonged sleep deprivation is a risk factor for depression.
- Genetics: People are more prone to developing dementia if there’s a family history of it, particularly with a close family member like a parent or sibling. If someone in your immediate family has the gene mutation for dementia, you’re 50% more likely to have it, too.
- Heart problems: There’s evidence suggesting that heart disease can increase the risk of dementia. Risk factors for heart disease include diabetes, high cholesterol levels, high blood pressure, and obesity.
- Medication: Certain heartburn medication, like Nexium, may increase the risk of dementia, as well as heart and kidney problems. It’s important to know what medications you’re taking and their risk factors. You should also know exactly how to take the medications you’re prescribed – it’s possible that misuse of the medication, not the medication itself, is responsible for adverse side effects, like a higher risk of dementia.
Until the right pharmaceuticals are created or discovered, the best options for patients are to use the medications that are currently available and to stay socially active. Improving overall health may help, too. Anything that keeps the brain healthy can help prevent depression, from getting more sleep to eating your veggies.
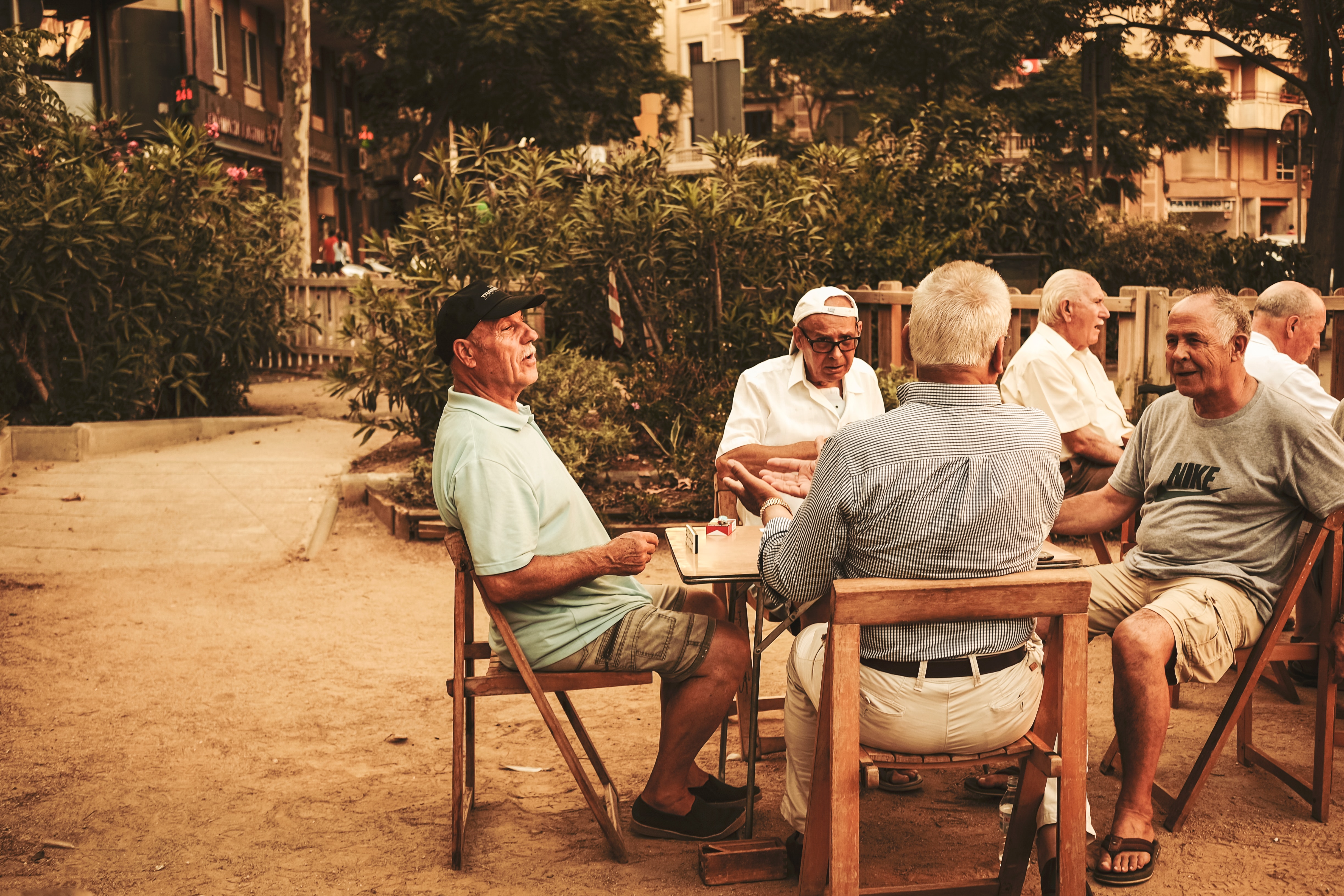
Social Contact May Reduce the Risk of Dementia
One of the top ways to keep depression at bay is to stay socially active, especially as you age. A study published in the PLOS Medicine journal shows that 60-year-olds who saw their friends almost daily reduced their risk of dementia by 12% when compared to people who saw a friend or two every few months. There were similarly strong connections between social contact and dementia in people aged 50 and 70. While there’s more research to be done when it comes to dementia and social life, reducing isolation and loneliness while exercising cognition through interaction can delay dementia symptoms. Overall, physical health and mental wellbeing can reduce the risk of dementia in some people.
How Health Professionals Are Working to Stop the Spread of Dementia
Experts are always conducting studies of dementia and working on treatments for it, but there’s still no known cure. Cholinesterase inhibitors are a type of drug that can improve symptoms for about a year and a half, but after that point, patients often have a decline again. Health practitioners should stay up-to-date with the latest education about dementia, including the specific requirements for dementia training, which vary by state. Currently, Nevada is one of the most dementia-friendly states, with initiatives for raising awareness and offering care partners to those living with dementia.
Unfortunately, there’s still no guaranteed way to ward off dementia, and for some people, it’s an inevitable truth. As research continues, the hope is that medical experts will one day find a cure. For now, the outlook isn’t as bleak as you may expect, though – according to Scientific American, men and women over the age of 65 have a good chance of remaining healthy for at least 12 years, and that time span is increasing.
Even if some symptoms of dementia emerge, many seniors are still able to have an enjoyable life. Since one of the best ways to prevent or slow down dementia is through social contact, seeing friends and family on a regular basis should be part of every aging person’s normal life.